Aim- What is Docker and Docker Compose. I will try to explain about linux container then goes more into Docker and Docker Compose for a beginner.
Now in this cloud buzz world, what developers want –
● Scalability, maintainability, Agility, Portability.
● DevOps tools.
● Improved resource utilization.
● A continuum of abstraction levels.
Linux Containers -contain applications in a way that keep them isolated from the host system that they run on. Containers allow a developer to package up an application with all of the parts it needs, such as libraries and other dependencies, and ship it all out as one package. And they are designed to make it easier to provide a consistent experience as developers and system administrators move code from development environments into production in a fast and replicable way.
In a way, containers behave like a virtual machine. To the outside world, they can look like their own complete system. But unlike a virtual machine, rather than creating a whole virtual operating system, containers don’t need to replicate an entire operating system, only the individual components they need in order to operate. This gives a significant performance boost and reduces the size of the application. They also operate much faster, as unlike traditional virtualization the process is essentially running natively on its host, just with an additional layer of protection around it
Linux Containers
● Use Linux kernel isolation features to give a VM like environment.
● Process isolation /Sandboxing.
● Example: Lxc, lmctfy, Docker.
Now, What is Docker –
● An easy to use Linux container technology.
● Docker image format.
● It helps in application packaging and delivery.
Docker is a tool that can package an application and its dependencies in a virtual container that can run on any Linux server. This helps enable flexibility and portability on where the application can run, whether on-premises, public cloud, private cloud, bare metal, etc. (Wikipedia)
Docker Vs Virtualization-
– Docker is lighter than virtual machines.
– The size of Docker images is very small compared.
– We can run more Docker container on a reasonably sized host.
– Deploying and scaling is relatively easy.
– Docker has less start up time.
Technologies behind docker
● Control groups:
○ Control Groups are another key component of Linux Containers
○ With Cgroup we can implement resource accounting and limit.
○ Ensure that each container gets its fair share of memory, CPU, disk I/O.
○ Thanks to Cgroup, we can make sure that single container cannot bring the system down by exhausting resources.
● Union file systems: ○ Layered file system so you can have a read only part and a write part, and merge those together. ○ Docker images made up with are layers.
● Namespaces
○ It helps to create an isolated workspace for each process.
○ When you run a container, Docker creates a set of namespaces for that container.
● SELinux
○ SELinux provides secure separation of containers by applying SELinux policy and labels.
What are components of Dockers
● Docker Images – An image is an inert, immutable, file that’s essentially a snapshot of a container. Images are created with the build command, and they’ll produce a container when started with a run. Images are stored in a Docker registry such as registry.hub.docker.com
● Docker containers – is an open source software development platform. Its main benefit is to package applications in “containers,” allowing them to be portable to any system running the Linux operating system
● Docker Hub – is a cloud-based registry service which allows you to link to code repositories, build your images and test them, stores manually pushed images, and links to Docker Cloud so you can deploy images to your hosts
● Docker Registry -is a cloud-based registry service which allows you to link to code repositories, build your images and test them, stores manually pushed images, and links to Docker Cloud so you can deploy images to your hosts
● Docker daemon -This is the part which does rest of the magic and knows how to talk to the kernel, makes the system calls to create, operate and manage containers, which we as users of Docker dont have to worry about.
● Docker client – This is the utility we use when we run any docker commands e.g. docker run (Docker container run), Docker images, docker ps etc. It allows us to run these commands which a human can easily understand.
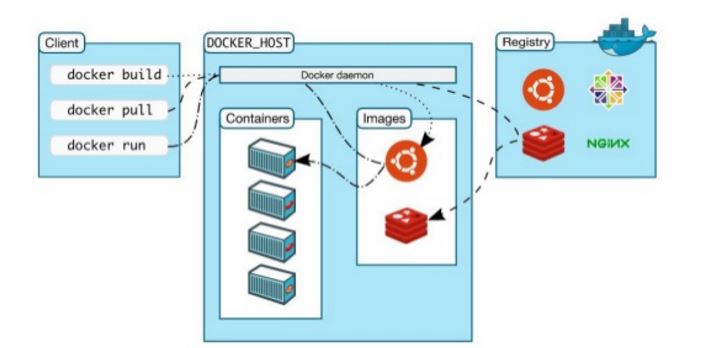
As you see above screen shot, we have docker client where the user performs build, pull and run operation.The client interacts with a host which contains different container, Docker Daemon and images via Registry.
If you guy reading this line, then you must be getting something about docker now. You know basic components and vocabulary.
Now let’s take an example of real life applications.
● One application consists of multiple containers.
● One container is dependent on another.
● Mutual dependency/ startup order.
● Process involves building containers and then deploy them
● Long docker run commands
● Complexity is proportional to the number of containers involved
![]()
Take example of above image, this will look multicontainer docker .The containers include (1) NGINX container, (3) Tomcat containers, (1) MongoDB container, and (1) ELK container. But have’t docker came to help us, This look quite difficult process to manage it all. To rescue us, Docker Compose is there.
Docker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. With Compose, you use a Compose file to configure your application’s services. Then, using a single command, you create and start all the services from your configuration.Compose is great for development, testing, and staging environments, as well as CI workflows.

Docker Compose
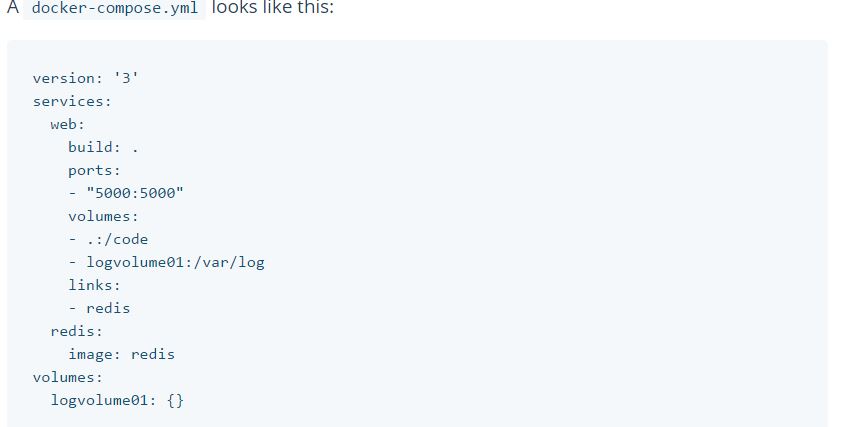
● Tool for defining and running multi-container Docker application.It is a YML file and compose contains information about how to build the containers and deploy containers. It is integrated with Docker Swarm. It competes with Kubernetes.
Compose is basically a three-step process.
1- Define your app’s environment with a Dockerfile so it can be reproduced anywhere.
2- Define the services that make up your app in docker-compose.yml so they can be run together in an isolated environment.
3- Lastly, run docker-compose up and Compose will start and run your entire app.
You can explore more with Docker Swarm, which I will explain in next post. Till then happy learning with Vinay